The "Doherty Threshold" is a term used in user experience (UX) design. This UX law, which has Walter J. Doherty's name as a tribute, plays an important role in deciding how we engage with digital products and services.
To develop seamless and effective user experiences, designers and businesses must understand the Doherty Threshold. In this article, we will discuss the Doherty Threshold, look at examples of it in practice, and highlight two case studies of businesses that have effectively applied this UX principle.
The Doherty Threshold Unveiled
Let's understand the Doherty Threshold law before moving on to real-world applications.
In the 1980s, IBM researcher Walter J. Doherty introduced this idea as a principle for human-computer interaction. According to the Doherty Threshold, a system's reaction time rise is closely related to a drop in user productivity and satisfaction. This means the longer the system takes to respond, the faster the user becomes uninterested. Productivity is at its peak when the interaction period between the user and system is less than or equal to 400 milliseconds because the attention span of people is decreasing day by day. So, if the system doesn’t respond quickly, the user can lose interest and choose a substitution system.
In simpler terms, the longer a user has to wait for a digital system to respond to their actions, the more frustrated and less productive they become. This idea matters because it highlights how important responsiveness and quickness are to UX design. Let's see how this idea functions in real life.
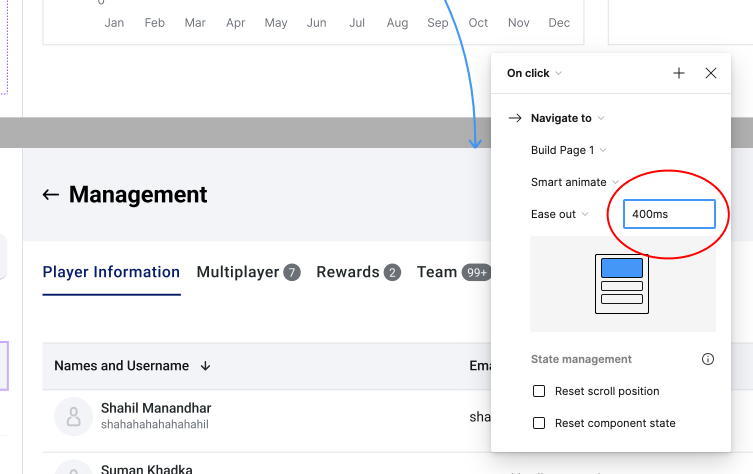
Human Psychology in Doherty Threshold Law
Human psychology is closely associated with the Doherty Threshold law, which highlights the effect of system responsiveness on user experience. This principle's relationship to human psychology can help us better understand its importance and the ways in which it affects user behaviour.
The following are some significant psychological elements of the Doherty Threshold:
Perception of Time
The way people perceive time varies. Users have a built-in timer when interacting with digital systems, and they want nearly immediate results. Users who experience delays longer than this imagined limit may become impatient and frustrated since it seems like they are waiting forever.
Frustration and Impatience
Negative emotional reactions may be caused by delays in the system's response. Users become impatient and frustrated when they believe their time is being wasted. These feelings may cause users to become less satisfied with the system or program and even leave it completely.
Cognitive Load
System slowdowns or responsiveness add to mental stress. Users have to maintain a record of their actions, intentions, and the system's status throughout the delay. This extra cognitive work may result in mental stress and poor task performance.
Instant Gratification
People today have been socialized to know about quick responses. Due to this behavioural characteristic, users demand quick responses and instant feedback in digital interactions. Users are usually more effectively satisfied by systems that meet this expectation.
Habituation
Users can grow habituated to systems that respond quickly. When people receive a lot of responsiveness, they start to take it for granted. Users may feel dissatisfied if a system starts to operate less responsively because they have grown used to a specific level of speed.
Real-Life Applications of the Doherty Threshold
Case Study 1: Google Search
Google is one of the most powerful companies that follow this principle. Keeping UI as simple as possible so the users know where to search without getting engaged in other components such as the navigation bar, footer or some type of animation. In addition to that, the servers are so powerful search results are presented in milliseconds. Giving people super-fast search results is the main objective of Google's search engine. Google knows that users searching for information online appreciate effectiveness and quickness.
To fulfil this request, Google regularly improves its servers and algorithms to deliver search results in milliseconds. The Google search homepage's simplistic design helps consumers conduct their queries quickly and with the least distraction. Google continuously exceeds customer expectations by placing a high priority on speed and responsiveness. The fact that Google dominates the search engine industry is largely due to its dedication to the Doherty Threshold.
Case Study 2: Amazon
To improve user experiences, the global online retailer Amazon has adopted the Doherty Threshold's guiding principles. One of the main reasons Amazon is successful is because of its one-click purchasing feature. With the help of this feature, registered users can buy something with only one click, skipping multiple steps and questionnaires.
Amazon strongly increases the speed and eases the purchasing experience by reducing the number of clicks required to complete a purchase. The Doherty Threshold's focus on reducing user wait times and increasing productivity aligns with this.
In addition, Amazon applies machine learning algorithms to recommend items to users, cutting down the time spent searching for items and improving the effectiveness of the shopping process. By implementing these strategies, Amazon has developed an interactive and user-friendly e-commerce platform that attracts repeat business.
The Doherty Threshold in Today's UX Landscape
The importance of Doherty Threshold is still important today, even with the rapid advancement of technology. Users have more expectations than ever for speed and responsiveness, so companies must constantly work to meet and exceed these demands to stay profitable.
The Doherty Threshold has also developed to consider overall user flow, intuitiveness, and reaction times. It's just as important to design user interfaces that are simple to use and demand minimal mental effort as it is to decrease response times. Organizations like Google and Amazon have perfected this complete method of UX design.
Thank you for reading! Subscribe to learn more about the different UX laws.
