Nowadays, hardly a day goes by without hearing the news of someone or some big corporation getting hacked. How is mass breach still a thing with increased security awareness and practices, advanced security measures, and multiple security standards an organization adopts? The answer is people. If you look into the recent breaches, you will often notice the same pattern behind successful attacks, i.e. social engineering.
- According to TechTarget, 80% of cyber attacks are the result of phishing scams.
- According to Cisco, 90% of all data breaches are because of phishing attacks.
- According to Forbes, 80% of reported incidents are tied to phishing attacks.
What is Phishing?
Phishing is a type of cybercrime where the attacker poses as a legitimate institution and sends fraudulent messages. The attacker's motive is to either gather an individual's personal information like credit card details, passwords, etc. or to infect the victim's device/s with ransomware. They are usually approached through phone calls, emails or text messages.
Why is Phishing So Effective?
The reason behind the success of phishing attacks becomes clear once you know the numbers. According to a recent survey, there are at least 4 billion email users worldwide. Malicious actors just need a casting net wide enough to get someone phished. Since it's pretty easy to find out the emails of people (social media for the win), everyone has access to millions, if not billions, of emails. With this information, they can mass send phishing emails to millions of people, hoping someone falls for it.
Common Red Flags
In this article, we will go through one of the common phishing attempts and analyze it for common red flags to look out for.
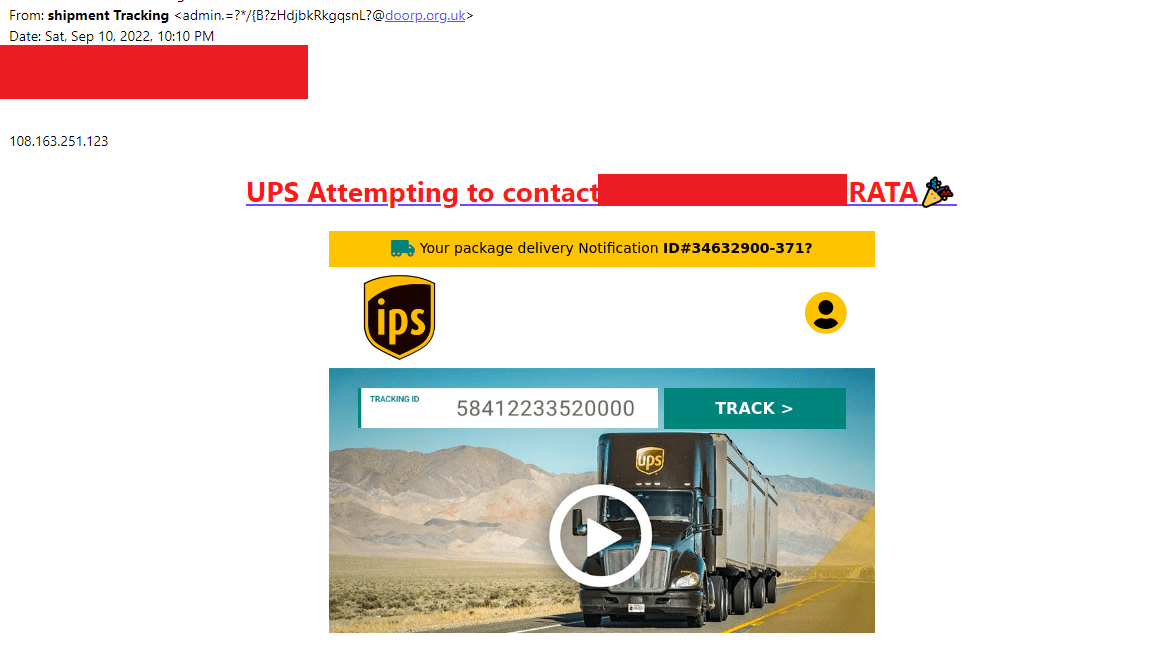
1. Senders Email
One of the first things you should do is look at the sender's email. Most organizations send mail to their customers using the example@organizations_name.com format or its variations.
In the image below, the sender's email ended with doorp.org.uk, which is not a valid email used by UPS.
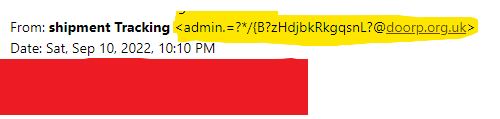
Do not blindly trust mail because it seems to be from valid emails. The attacker might have compromised the email or spoofed it to look like it came from a legit source.
2. Design Flaws
These phishing emails often contain design flaws. It might be in the form of distorted graphics, irregular logos, misspellings, etc. They might go unnoticed at a quick glance but becomes obvious once you take a step back and analyze them slowly. In the image below, they changed the alphabet in the logo.

3. Deceptive Links
Malicious actors cannot do anything to harm you just by sending mail in most cases. So, they often trick you into clicking links that will download malware or redirect you to sites they control. Viewing your emails on a desktop allows you to hover over articles to reveal the underlying links without clicking.
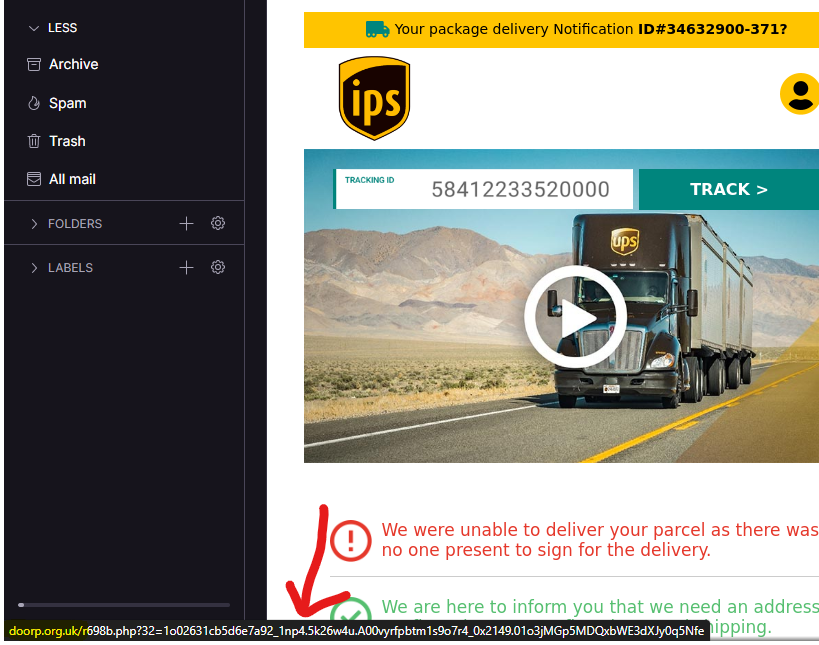
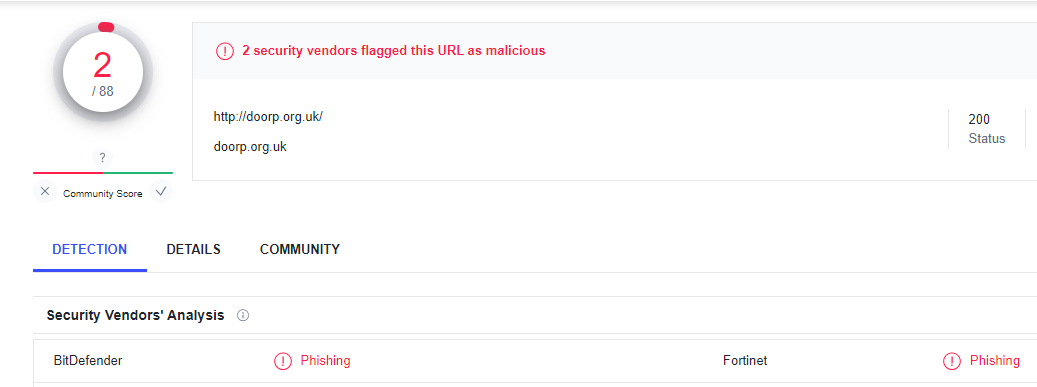
Are The Links Malicious?
There are various services available for free to know if the websites you visit are suspicious. For example, we fed the link from the above image to a Virustotal to check if they had been flagged. And it sure was, and we also know the reason why.
4. Irregularities
Phishing emails will most likely contain various irregularities as they are not meant for official businesses but to deceive you into clicking malicious links. As seen below, two unsubscribe prompts exist from two organizations in different locations.
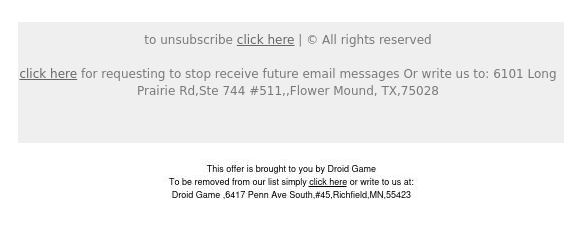
Looking further into them, we can see that they are not even texts but images that would redirect you to the same link from above when you click on it.

Email Security Tips
1. Delete Email Contacts You Don't Recognize
Solutions are often very simple. If you ever get mail from unknown contacts, send it straight to the trash (and clean it as well). If it seems suspicious, it is.
2. Use Multi-Factor Authentication
Do not ever rely on a single protection mechanism to keep you safe. At least turn on your two-factor authentication to protect your account.
3. Refrain from Opening Unexpected Attachments
Even if the mail came from a trusted source (your co-workers or friends), if it has an attachment, never download or click on it if you are not expecting it. Ask them first what the attachment is about. Do not reply to the mail. Confirm with them using different communication modes.
4. Avoid Using Your Email to Sign Up for Free Stuff
Who doesn't like free stuff? We all go feral when there is something we can grab for free. I won't say don't skip on free stuff but do it in a way it won't affect you. If the service requires you to provide email, use the burner email instead. Hundreds of sites provide temporary email for use. Just sign up using that mail and forget all about it.
5. Use Aliases
Most email services have an alias feature. You can use this feature when signing up for services. For example, if imt@example.com is your email, and you want to sign-up for pencil service, use imt+pencil@example.com. One advantage of using this feature is you will know the source whenever your email is compromised.
In Summary...
You now know that phishing is one of the most common attacks when it comes to cybercrimes. It can be very easy to deceive people with this attack as the attackers are very clever about the false image they put out to fool people. You cannot stop it, but you can prevent it using the security tips mentioned above. Watch out and stay safe!
Thank you for reading. Subscribe for more security related articles.
