The term 'entrepreneur' is formed by adding the suffix '-eur' to the French verb 'entreprendre,' which translates to "to undertake". The suffix turns the verb into an agent noun, signifying 'The one who undertakes'. This is an apt nomenclature since entrepreneurship encompasses the allocation of private capital as well as a substantial commitment of time and effort into the enterprise amid a flurry of risks associated with the market. This constitutes a considerable undertaking indeed.
The Evolution of Entrepreneurship
The evolution of the modern entrepreneur's role calls for modern ideas and business models. With the major changes in the past few years, the potential to amend the disruptions in the market ecosystem by addressing contemporary challenges and building more resilient supply flows that are responsible and equitable is crucial more than ever.
The risks of setting up a new business - market competency, the fear of risk capital, good investment and the hassle of starting a business must be dealt with and overcome. These risks demand new innovative ideas and inspire well-planned, calculated market risks that only a few have accomplished. Thus, a modern entrepreneur undertakes those ventures that blend well with the current demand and marketing needs.
Soon, we will experience a dynamic and entrepreneurial ecosystem where individuals and organisations actively identify, create, and pursue opportunities for innovation, value creation, and economic growth.
8 Types of E-commerce Business Models
It starts with recognising unmet social desires, leading to the inception of indigenous ideas that evolve into innovative products or services. They adapt and commercialise their ideas, taking calculated risks to establish successful enterprises.
The present economic climate necessitates inspiring new approaches that leverage SMEs (Small and Midsize Enterprises) and retailers. Here, we delve into pioneering trends and models of contemporary entrepreneurship.
The landscape of e-commerce in 2002 encompassed various business models, including:
Business-to-Business (B2B)
This refers to business transactions where one business sells products or services to another.
Business-to-Consumer (B2C)
In B2C, businesses sell products or services directly to individual consumers.
Consumer-to-Consumer (C2C)
C2C commerce involves individuals selling products or services directly to other individuals.
Consumer-to-Business (C2B)
C2B occurs when individual consumers offer products or services to businesses. This can include freelance work, influencer marketing, or user-generated content.
Direct-to-Consumer (DTC)
DTC refers to companies selling their products directly to consumers, avoiding traditional retail channels. This often occurs online, allowing brands more control over their customer relationships.
Social Commerce
Social commerce combines social media and e-commerce, allowing users to buy products directly through social media platforms or interact with shopping features integrated into social networks.
Subscription-Based E-commerce
In this model, customers pay a regular fee to access products or services. Companies deliver items regularly, such as subscription boxes or streaming services.
Peer-to-Peer (P2P) Sharing Economy
P2P sharing economy refers to individuals sharing resources directly with one another, often facilitated by digital platforms. For example, ride-sharing services like Pathao and Uber and home-sharing platforms like Airbnb.
E-commerce Platforms and Digital Marketing
E-commerce platforms such as Shopify, WooCommerce and BigCommerce provide user-friendly interfaces to set up online stores without requiring extensive technical expertise. This simplifies the startup process, allowing them to create a business profile and engage directly with their customers. Once a strong online presence is established, marketing or promoting business services and products becomes effortless. Thanks to digital marketing tools such as social media advertising and search engine optimisation.
Familiar social media platforms like Instagram and Facebook, among others, have played a pivotal role in connecting people and building a business's social presence. These social media platforms are equipped with analytical tools that are best for entrepreneurs, saving both time and money when it comes to analysing business growth or experimenting with multiple campaigns and ideas. Therefore, don't hesitate to take action and begin your entrepreneurial journey.
Supply Chain and Manufacturing Strategies
When manufacturers and retailers collaborate, they enhance the value they offer consumers. In today's competitive retail market, delivering customer value is the keystone for generating revenue in the industry. Modern markets demand a consistent commitment to staying updated on consumer and product trends.
Dropshipping: A Flexible Approach
Dropshipping constitutes an e-commerce business model where a retailer (the entrepreneur) markets products to customers without needing a physical inventory or a brick-and-mortar store.
Manufacturing companies sign agreements with wholesalers or other retailers to provide the goods they advertise. Easy put, it is a retail fulfilment method where sellers list products on their online store without having them in the inventory. So, only when a customer places an order does the seller purchase it from a third-party supplier and ship it directly to the customer.
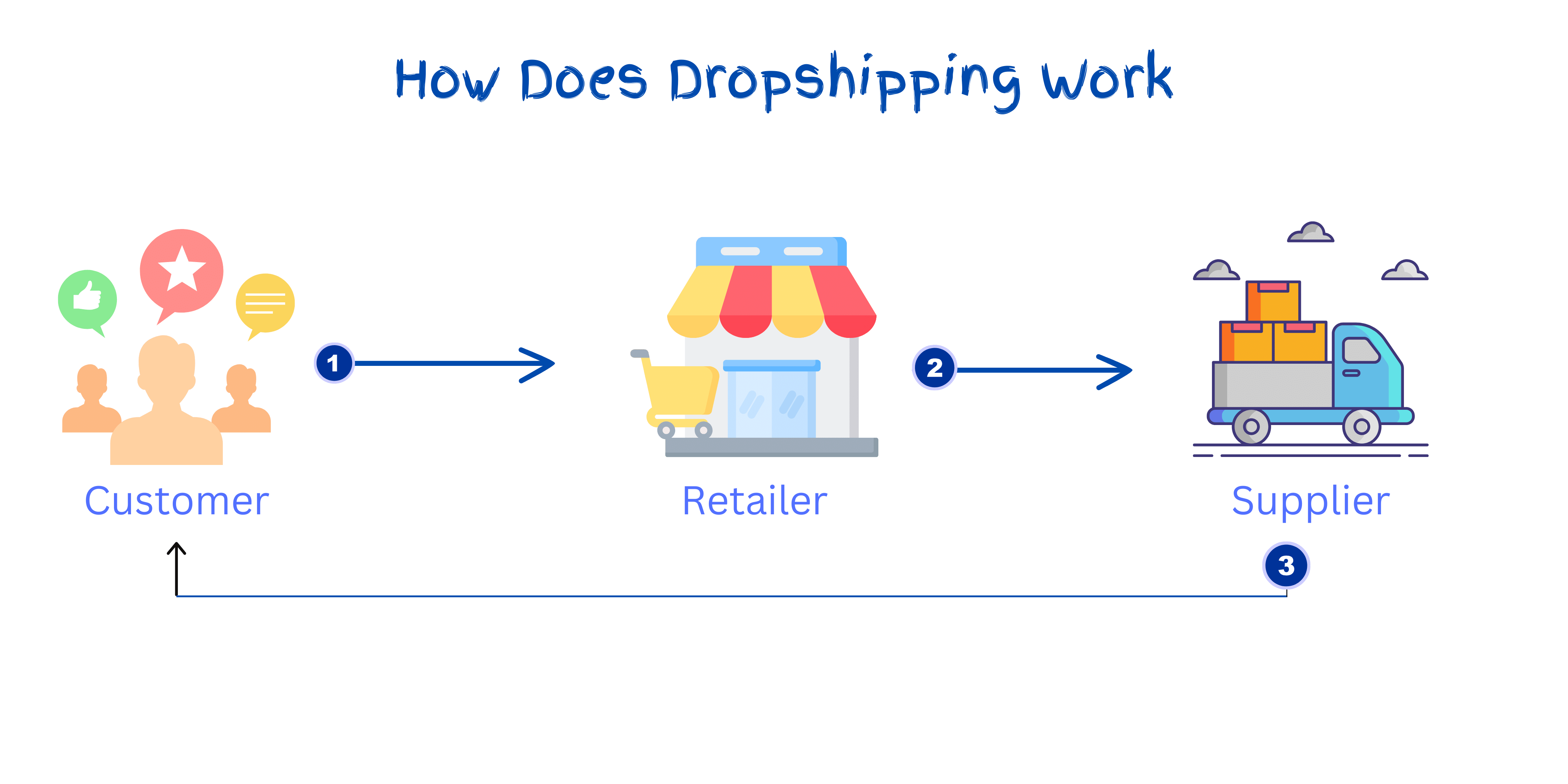
This flexible approach eliminates the necessity of owning a physical shop, making it a viable choice for startups aiming to venture into e-commerce with minimal upfront investment and risk.
It particularly appeals to those valuing flexibility, dealing with limited storage capacity, and wishing to test multiple products without committing to large quantities. However, due to its lower profit margins and potential challenges related to quality control and customer service, entrepreneurs must diligently research suppliers and plan their strategy to stand out in a competitive market.
Wholesaling and Warehousing: Distribution Dynamics
Wholesaling and warehousing represent two distinct yet closely related business models within the supply chain and distribution industry.
Wholesaling involves purchasing large quantities of products from manufacturers or suppliers and then selling those goods in smaller quantities to retailers, other businesses, or directly to consumers. The primary objective of wholesalers is to act as intermediaries connecting consumers with manufacturers.
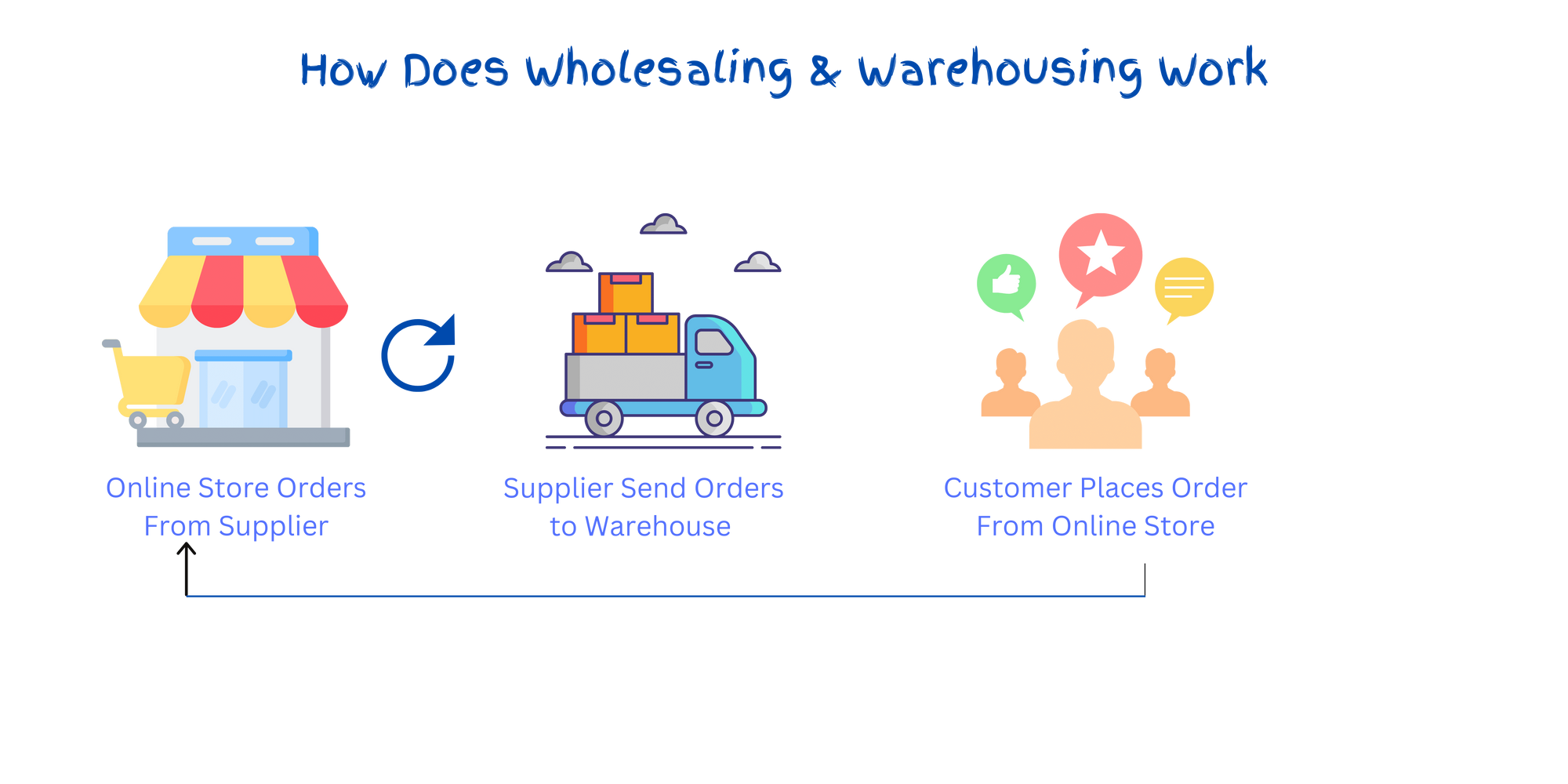
In the contemporary business landscape, modern entrepreneurs employ technology-driven approaches to engage in wholesaling. They leverage distribution channels like direct sales and online platforms to reach a broader customer base. Establishing a wholesale business necessitates a substantial budget for a startup. However, once established, wholesalers enjoy advantages over retailers and manufacturers as they can select their product offerings, including seasonal, trending, valuable or high-demand goods.
Moreover, modern wholesalers adapt to the e-commerce landscape by providing customers with a reliable and user-friendly online shopping and selling experience, complete with multiple payment methods for global companies and merchants. For example, Alibaba is one of the world's largest wholesale online shopping platforms, providing small and midsize business buyers with access to branded products from reputable suppliers.
Commercial buildings or warehouses are utilised to facilitate the storage of products and goods before distribution. Warehousing has evolved into a critical asset that serves the needs of manufacturers and retailers and aids modern manufacturers in both before and after production.
Warehousing focuses on holding and managing the raw materials for manufacturers before production and distributing the finished goods to the market after production on behalf of manufacturers, wholesalers, retailers, or e-commerce businesses. Therefore, it plays a pivotal role in the supply chain by safeguarding products until they are required for distribution.
Modern warehousing integrates technology to enhance storage efficiency. This involves implementing numerous automated systems, scheduling processes, packaging methods, real-time monitoring tools, and other smart solutions for optimising inventory management and supply chain. For example, DHL Supply Chain offers extensive warehousing and distribution services, including inventory management, order fulfilment, and transportation, to help businesses streamline their supply chain operations through technology-driven solutions.
Private Labelling and Manufacturing: Branding Your Way
Private labelling involves procuring products from a third-party manufacturer and selling them under a retailer's brand name. Generally, it is the practice of marketing products under your unique brand identity. This approach offers numerous advantages for retailers in the current competitive market. National brands increasingly promote private labels and incorporate them into their market offerings.
Private Label Manufacturers companies produce products for other companies/retailers to sell under their brand name. Unlike white labelling, which we will get into later, private label manufacturers offer exclusivity and customisation facilities per the retailers' demand, allowing you to create a unique product under your brand name.
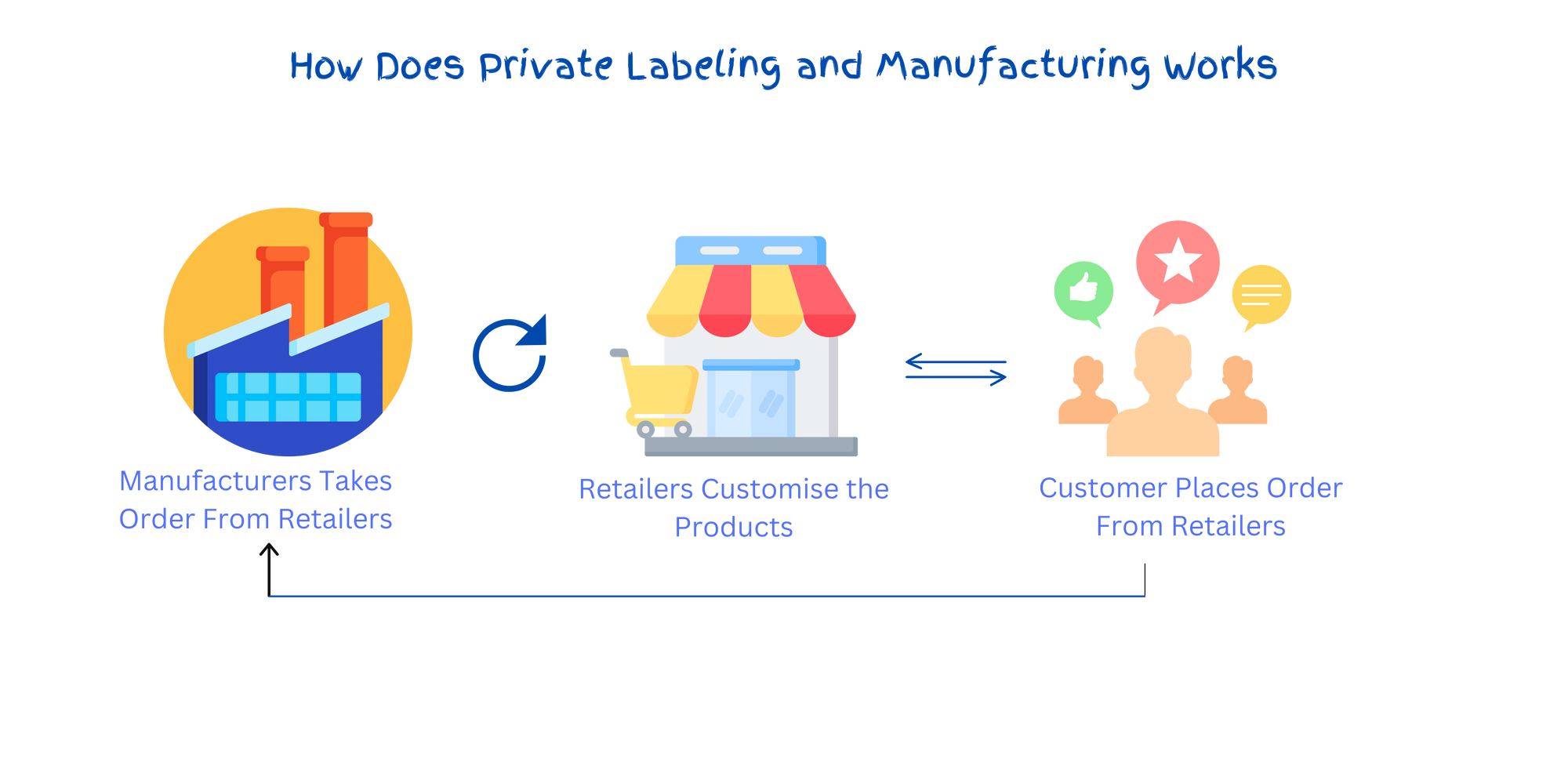
The whole process of product development, manufacturing, packaging and shipping is handled by the private label manufacturers and the remaining parts- branding, sales and marketing, customer support/experience, and distribution are to be handled by retailers.
A cost-effective model is crucial for small businesses and startups, allowing them to allocate resources wisely. This model grants them control over product development and branding, enabling them to shape their identity in the market. Moreover, having control over product pricing leads to higher profit margins, a key advantage for emerging enterprises. These businesses can further enhance their market positioning and success by conducting even a modest amount of product research.
The challenge lies in finding reliable and affordable private-label manufacturers. Several online platforms connect private label manufacturers with entrepreneurs; for example, Alibaba offers a wide range of private label manufacturers and suppliers worldwide. With extensive products and easy communication facilities with manufacturers, it is an excellent choice for entrepreneurs. Select a proper private-label manufacturer with established relationships with retailers that produce high-quality products and meet your brand's standards.
Also, the Private Label Manufacturers Association (PLMA) is a valuable resource for contemporary retailers aiming to harness the benefits of private labelling. The PLMA can assist retailers in bringing their brand vision to life, identifying reputable manufacturers meeting their quality and safety requirements, and establishing connections with manufacturers capable of efficiently producing customised products.
White Labelling and Manufacturing: A Cost-Effective Alternative
Like private labelling, white labelling constitutes an e-commerce business model in which a retailer (the entrepreneur) procures products from third-party manufacturers in bulk or as custom orders. Then retailer rebrands these products with their logos or branding and sells the final product to customers.
The main difference between private and white labelling is that private label manufacturing is exclusive to one retailer, while white labelling allows manufacturers to sell the same product to multiple retailers, making it not the exclusive property of a single retailer. The other difference lies in the limit over customisation; under white labels, retailers have no control over the product details and must accept the manufacturer's product as is.
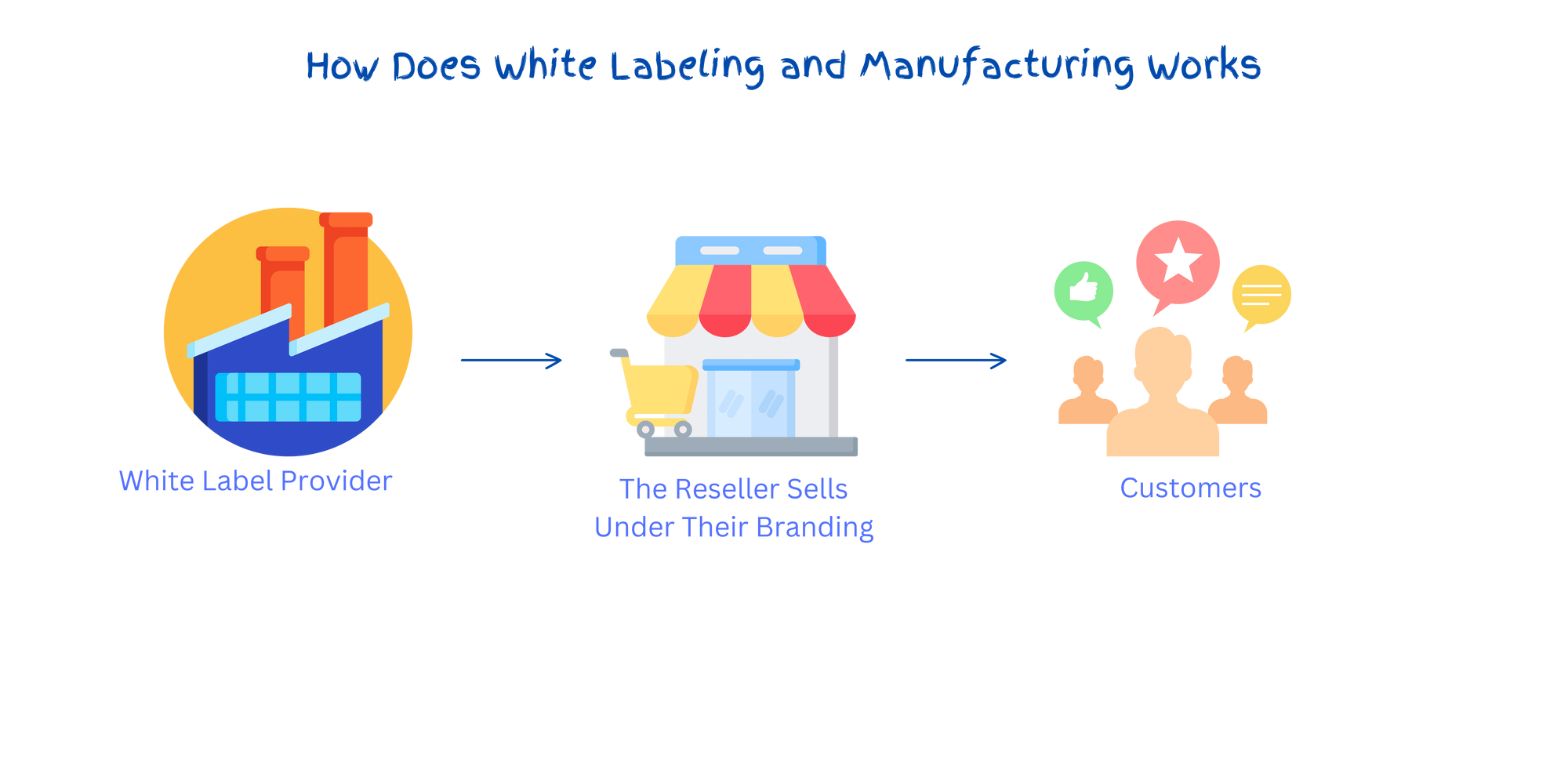
This practice is often executed in bulk, such as purchasing plain T-shirts, rebranding them with custom logos or designs, and then marketing the final product to customers. This allows them to enter the market without the complexity and cost of developing their own products. The white-label manufacturer, in turn, can sell the same products to other retailers under their respective branding, making it a win-win for both parties.
Choosing the Right Revenue For Your Startup
Selecting the ideal revenue model for your business is a critical decision that can significantly impact your success. There is no one-size-fits-all answer, and your choice should align with various key factors:
- Nature of Your Product/Service: The type of product or service you offer should drive your revenue model choice. Different models, such as subscriptions for SaaS or diverse strategies for e-commerce, cater to specific offerings.
- Understanding Your Target Audience: Tailoring your pricing strategy to match your target audience's preferences and willingness to pay is crucial for success.
- Analysing the Competitive Landscape: Studying competitors and their revenue models enables you to differentiate your business by offering unique pricing and monetisation strategies that set you apart.
- Calculating Customer Lifetime Value (CLV): Evaluating CLV under various revenue models is essential for sustainable growth and profitability, emphasising the long-term value of customer relationships.
- Monitoring Market Trends and Regulations: Staying informed about market trends and regulations is vital, allowing adaptability to navigate evolving conditions effectively.
- Embracing Testing and Adaptation: Experimentation and adjustment based on customer feedback and performance metrics are encouraged. Flexibility and adaptation are crucial in the dynamic business landscape.
Conclusion
Entrepreneurs are encouraged to leverage innovation, technology, and global markets while considering diverse e-commerce models like on-demand manufacturing, dropshipping, wholesaling, warehousing, private labelling, and white labelling.
This article explored the essence of entrepreneurship, its evolution in the modern world, and the critical factors defining the role of contemporary entrepreneurs. We also delved into various e-commerce models and revenue strategies that have been proven successful in recent times. Ultimately, the article has highlighted the importance of adaptability and innovation in driving economic growth and addressing modern challenges in our interconnected society.
Thank you for reading! Subscribe to our devblog and don't miss out on other insightful blogs.
