Kubernetes has become the de facto standard for container orchestration and has been widely adopted by organizations of all sizes. With the rise in microservices, managing deployments and ensuring continuous integration and continuous delivery (CI/CD) has become critical aspects of software development. This is where ArgoCD comes in. In this blog, we will discuss how to perform CI/CD on a Kubernetes cluster using ArgoCD.
Methods of Deploying ArgoCD
ArgoCD is an open-source GitOps tool that helps automate application deployment in a Kubernetes cluster. To get started with ArgoCD, it needs to be installed in the cluster. There are several ways to install ArgoCD, including the usage of a command line interface (CLI), a YAML file, or an ArgoCD Operator.
Requirements
In this blog, we will install ArgoCD using the CLI. First, you need to have kubectl and a working Kubernetes cluster installed. Once you have the prerequisites, run the following command to install ArgoCD:
kubectl create namespace argocd
kubectl apply -n argocd -f https://raw.githubusercontent.com/argoproj/argo-cd/stable/manifests/install.yaml
Deploying the App
Once ArgoCD is installed, you can deploy your app using ArgoCD. ArgoCD uses a Git repository to manage your application deployments. You need to have your app source code, and the Kubernetes manifests that describe the deployment, service, and ingress in the same Git repository.
Use the following command to perform port-forwarding to access the Argo instance locally:
kubectl port-forward svc/argocd-server -n argocd 8080:443Now fetch the Argo password using the following command:
kubectl -n argocd get secret argocd-initial-admin-secret -o jsonpath="{.data.password}" | base64 -dCreate a public Git repository to store the Kubernetes manifests from which Argo will create the applications. You can use any Git hosting service, such as GitHub or GitLab, to create the repository.
We must provide the manifest(s) defining resources that will make up our application, such as pods, services, ingress rules, etc. Commit the manifest to your Git repository and push it to the remote repository. For now, you can use this Git repository. It contains manifests for an Nginx Web Server.
CLI Method
Step 1: Install ArgoCD's command line tool
brew install argocdStep 2: Log in to the Argo instance on Kubernetes
Command:
argocd login localhost:8080
Output:
WARNING: server certificate had error: x509: certificate signed by unknown authority. Proceed insecurely (y/n)? y
Username: admin
Password:
'admin:login' logged in successfully
Context 'localhost:8080' updatedStep 3: Create the application
Command:
argocd app create nginx --repo https://github.com/nischal-subedi/cicd-kubernetes --path ./ --dest-server https://kubernetes.default.svc --dest-namespace nginx
Output:
application 'nginx' createdStep 4: Sync the application
Command:
argocd app sync nginxOutput:
TIMESTAMP GROUP KIND NAMESPACE NAME STATUS HEALTH HOOK MESSAGE
2023-02-21T11:13:30+05:45 Service default nginx-svc Synced Healthy
2023-02-21T11:13:30+05:45 apps Deployment default nginx Synced Healthy
2023-02-21T11:13:31+05:45 Service default nginx-svc Synced Healthy service/nginx-svc configured
2023-02-21T11:13:31+05:45 apps Deployment default nginx Synced Healthy deployment.apps/nginx configured
Name: argocd/nginx
Project: default
Server: https://kubernetes.default.svc
Namespace: default
URL: https://localhost:8080/applications/nginx
Repo: https://github.com/nischal-subedi/cicd-kubernetes
Target: HEAD
Path: ./
SyncWindow: Sync Allowed
Sync Policy: <none>
Sync Status: Unknown
Health Status: Healthy
Operation: Sync
Sync Revision: f1ae436b1b5406105feea6fa22ba3fca098af646
Phase: Succeeded
Start: 2023-02-21 11:13:30 +0545 +0545
Finished: 2023-02-21 11:13:31 +0545 +0545
Duration: 1s
Message: successfully synced (all tasks run)
GROUP KIND NAMESPACE NAME STATUS HEALTH HOOK MESSAGE
Service default nginx-svc Synced Healthy service/nginx-svc configured
apps Deployment default nginx Synced Healthy deployment.apps/nginx configuredStep 5: Check the status of the Argo app
Command:
argocd app get nginxOutput:
Name: argocd/ngninx
Project: default
Server: https://kubernetes.default.svc
Namespace: nginx
URL: https://localhost:8080/applications/nginx
Repo: https://github.com/nischal-subedi/cicd-kubernetes
Target:
Path: ./
SyncWindow: Sync Allowed
Sync Policy: <none>
Sync Status: Synced to (f1ae436)
Health Status: Healthy
GROUP KIND NAMESPACE NAME STATUS HEALTH HOOK MESSAGE
Service nginx nginx-svc Synced Healthy service/nginx-svc created
apps Deployment nginx nginx Synced Healthy deployment.apps/nginx createdGUI Method
Step 1: Access the login page
Open your browser and go to http://localhost:8080 to access the ArgoCD UI. Enter the username as admin and use the extracted password to log in.
Step 2: Create the application
Now click on the create application button and follow the images below.
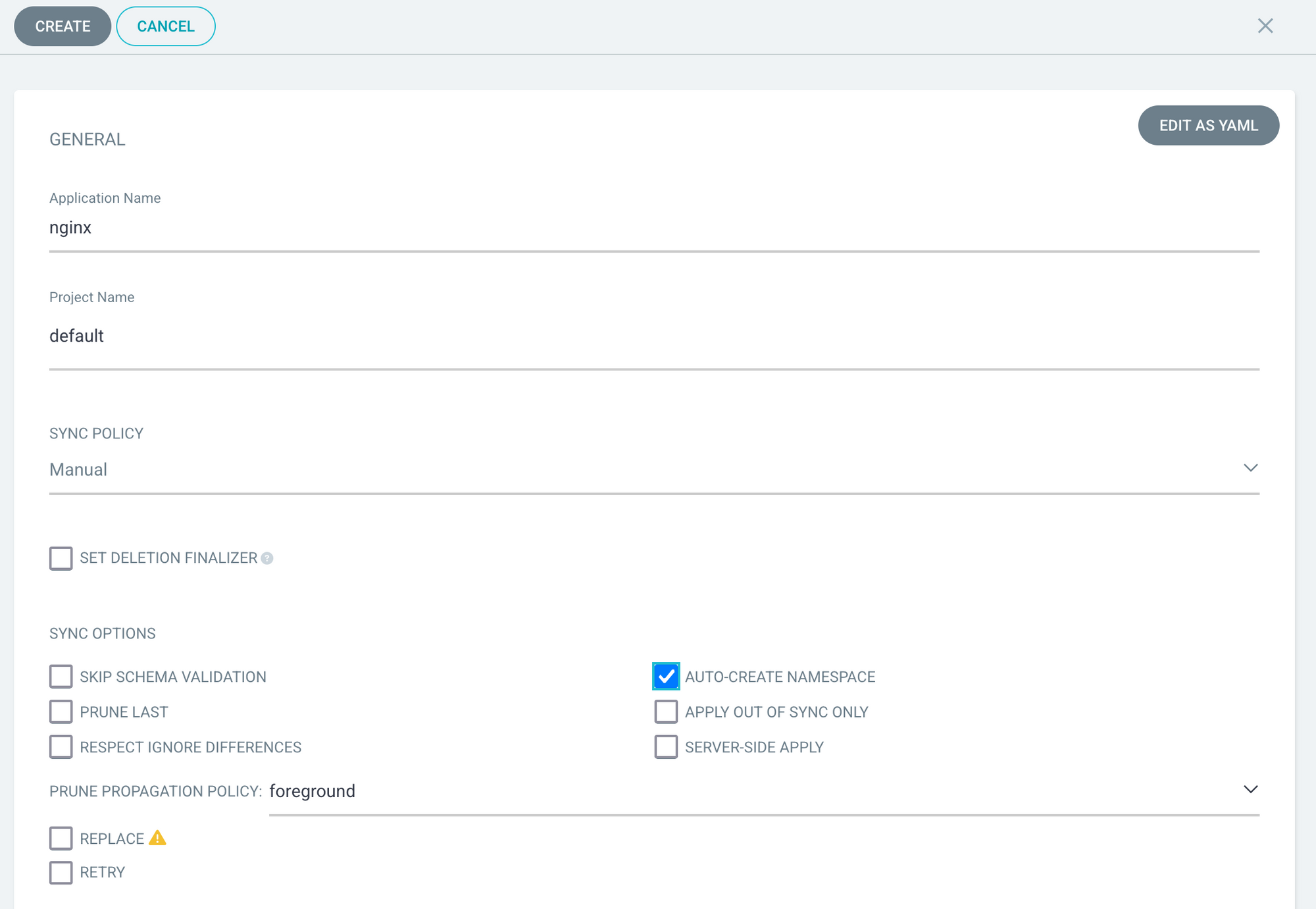
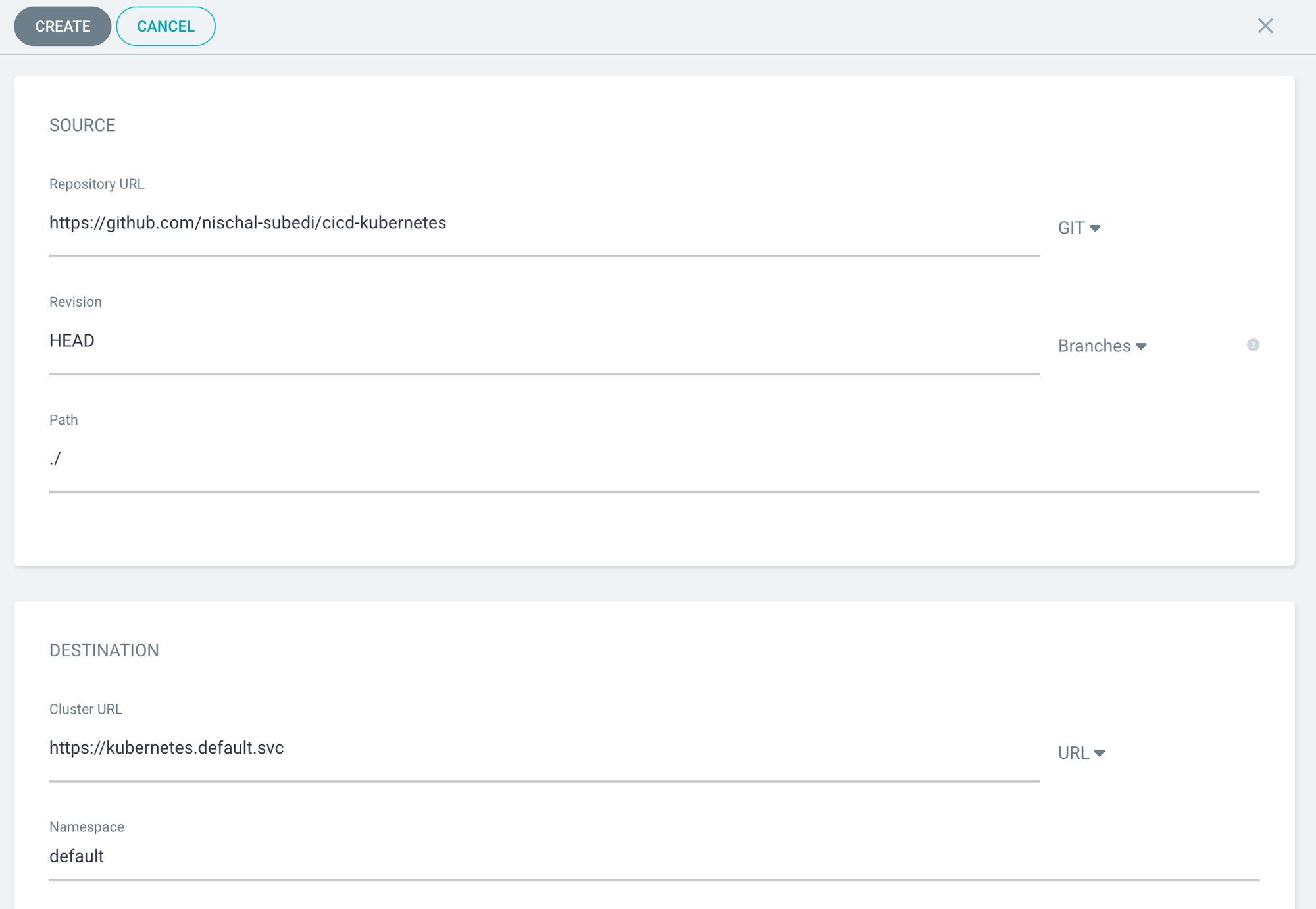
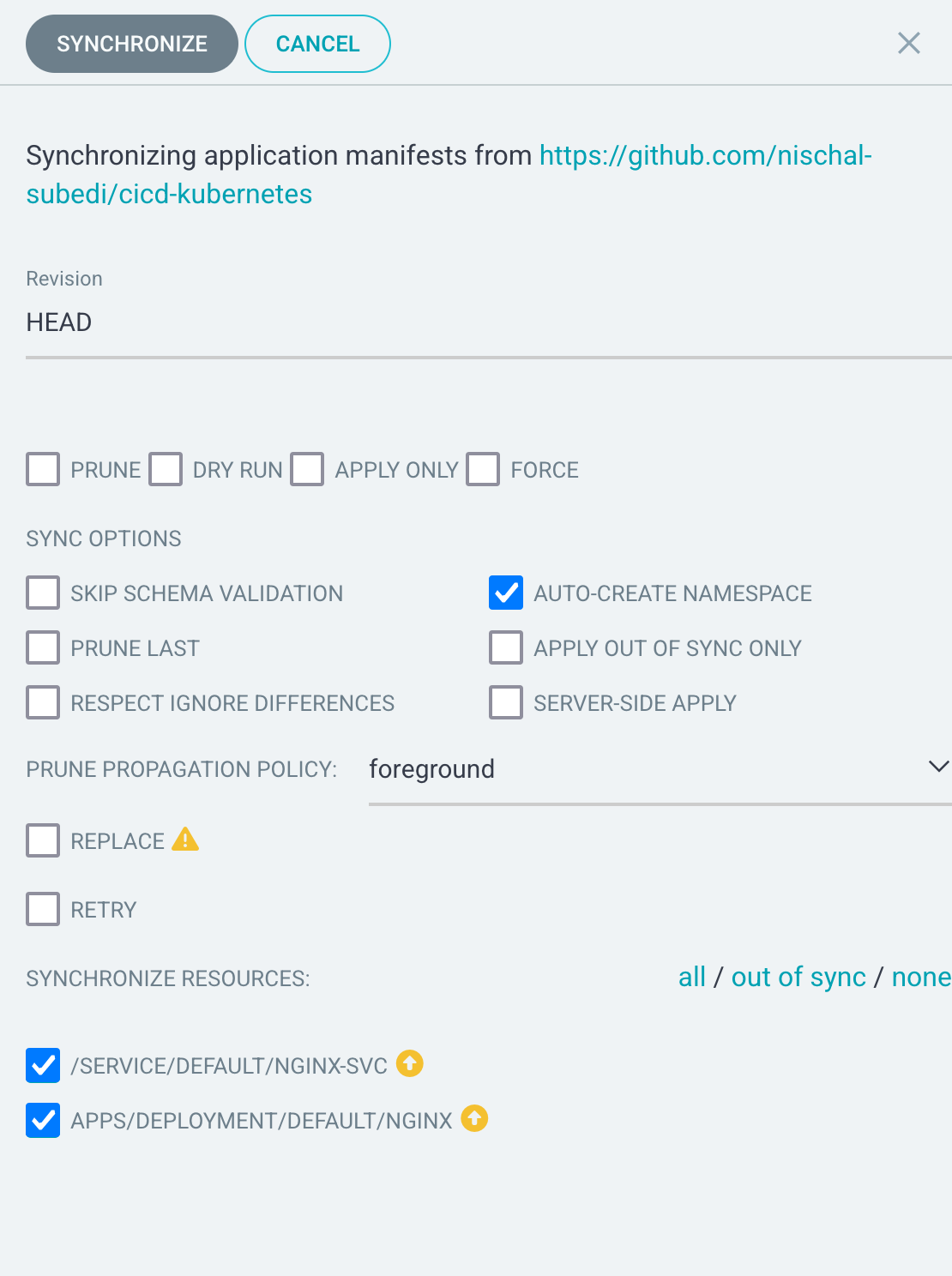
Step 3: Sync the application
Once done, click on the Sync button.
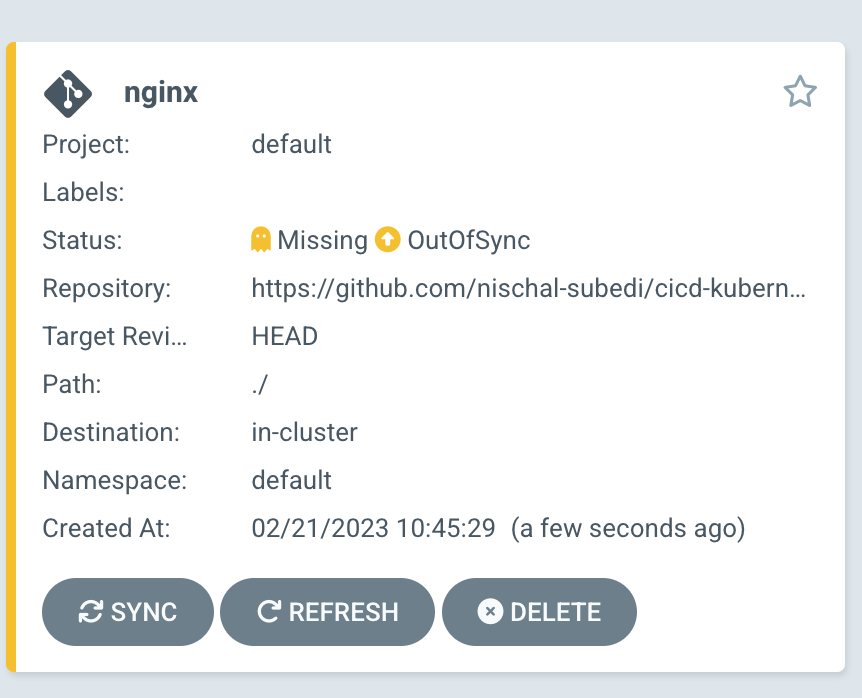
Step 4: Check the app status
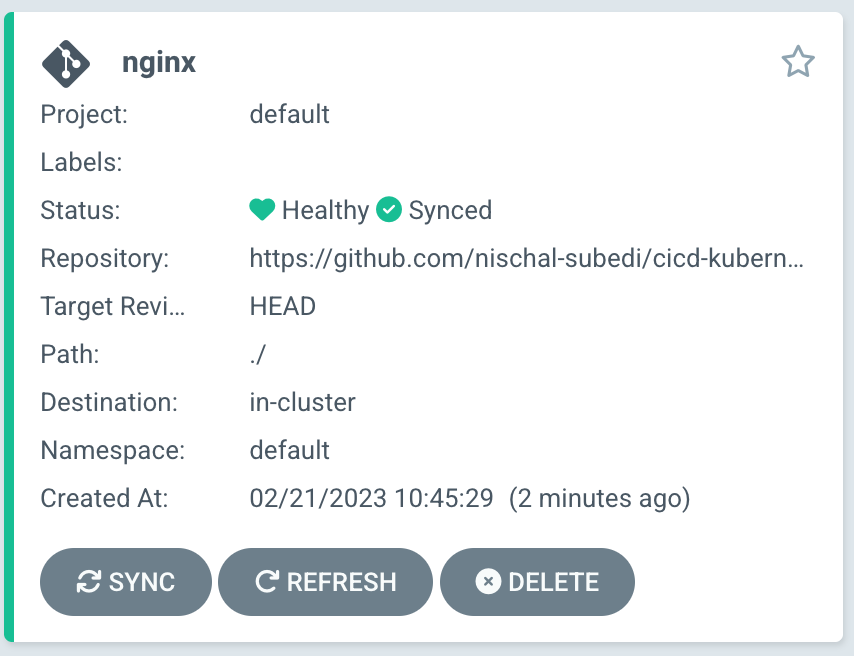
As this is a straightforward application, the app should immediately reach Healthy Status.
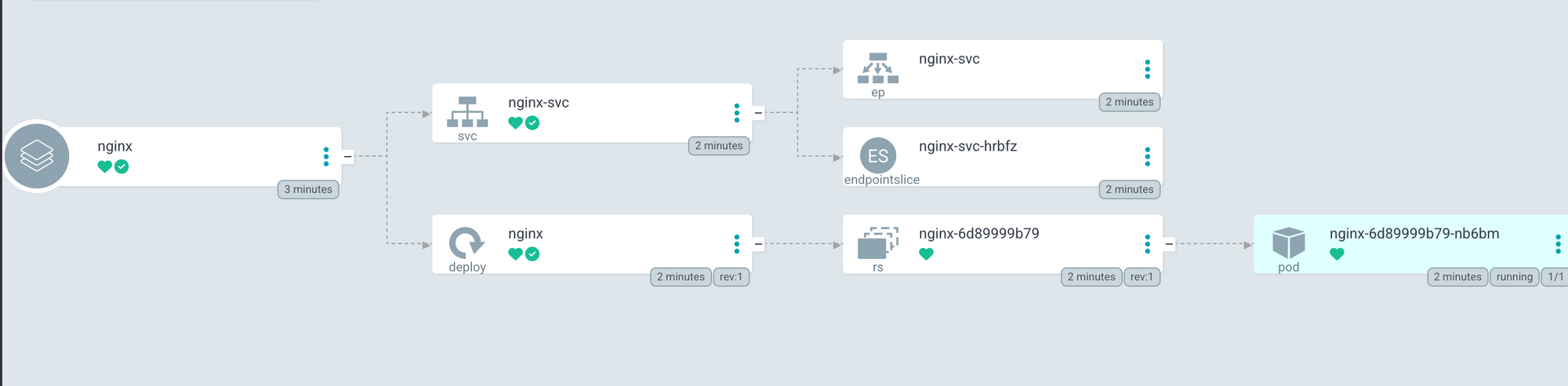
If you click on the app, you should see the resources being consumed in the node by the application, resource hierarchy, etc.
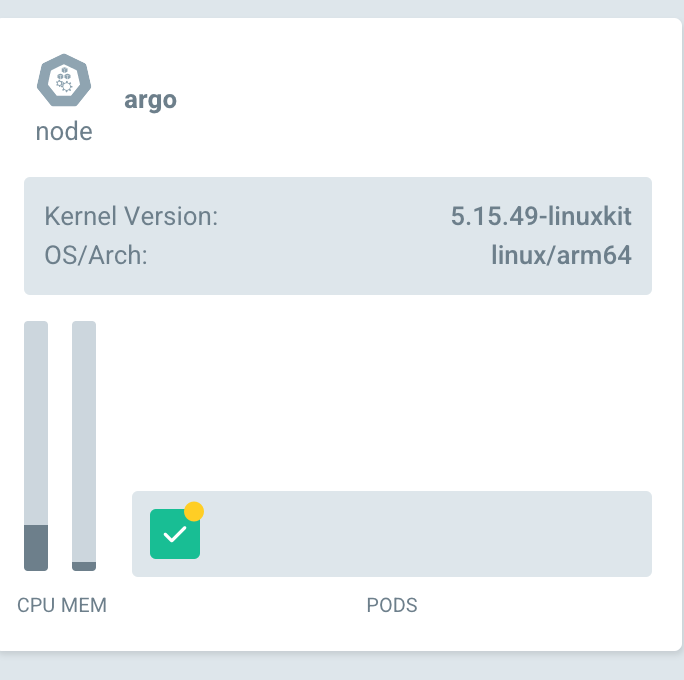
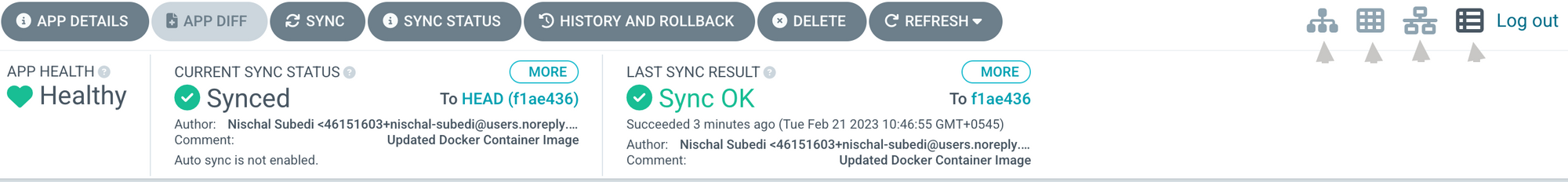
This all can be toggled in the top navigation bar beside the Log Out button. You can refer to the image shown below.
How does ArgoCD work?
Once we provide a repository to ArgoCD, it will continuously listen for any changes to the repository branch specified in the Argo Application.
Once a change is detected in the Kubernetes manifest of that branch (like pushing commits or merging changes from a different branch to the selected branch), Argo will apply the changes specified in the new Kubernetes manifest into the cluster. This can either be an update operation (kubectl apply) or a create operation (kubectl create).
Best Practices
ArgoCD provides several best practices when performing CI/CD on a Kubernetes cluster. Some of the best practices include:
Using GitOps to manage the deployments
GitOps is a great way to manage deployments in a Kubernetes cluster. It provides an auditable trail of all changes made to the deployments, making it easy to roll back to a previous version if needed.
Using namespaces to isolate environments
Make use of namespaces such as development, testing, and production. This makes it easy to manage different versions of the app and ensures that the deployments are isolated from each other.
Using Git branch protection
Use Git branch protection to merge only approved changes into the production branch. This helps prevent accidental deployments of untested code.
Frequently Asked Questions
1. What is ArgoCD?
ArgoCD is an open-source GitOps tool that helps automate the deployment of applications in a Kubernetes cluster. It uses Git repositories to manage the deployments and ensures they are always in sync with the Git repository.
2. How does ArgoCD work?
ArgoCD works by using GitOps to manage the deployments. It uses a Git repository to store the source code, and the Kubernetes manifests that describe the deployments, services, and ingresses. When changes are made to the Git repository, ArgoCD automatically syncs the changes to the Kubernetes cluster.
3. Can ArgoCD be used with other CI/CD tools?
Yes, ArgoCD can be used with other CI/CD tools, such as Jenkins, TravisCI, and CircleCI. The CI/CD tool can be used to build and test the app, and ArgoCD can be used to deploy the app to the Kubernetes cluster.
Conclusion
In this article, we learned about ArgoCD, its best practices, use cases and how it can be used to automate the deployment of an application in Kubernetes. In another article, we will learn to set up a complete CI/CD pipeline using ArgoCD.
Please comment below if you have any queries, and stay tuned for more on Kubernetes native CI/CD tools.
